Oats (Avena species of the Poaceae family) are annual herbaceous plants recognized globally as a multifunctional crop widely used in food, cosmetics, animal feed, medicine, and industrial applications. Rich in minerals, vitamins, balanced amino acids, unsaturated fatty acids, and unique water-soluble dietary fibers, oats stand out particularly because of Oat beta glucan, a highly studied and widely applied non-starch soluble fiber.
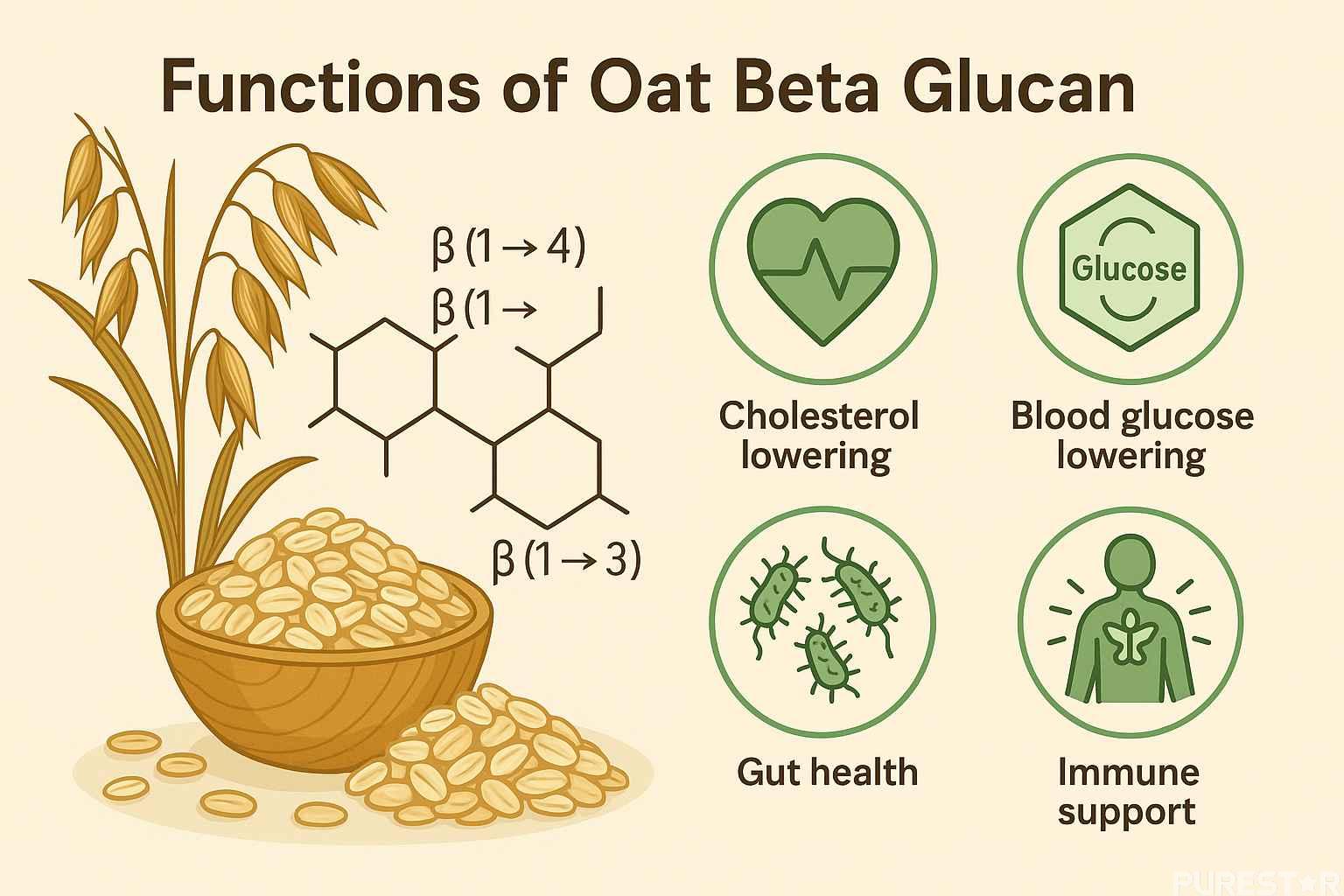
Oat beta glucan—found mainly in the aleurone and subaleurone cell walls—is a linear polysaccharide composed of β(1→3) and β(1→4) linkages of β-D-glucopyranose. As a relatively low-molecular-weight glucan, it exists as a short-chain soluble fiber with excellent physiological properties. Among cereal crops, oats contain the highest natural concentration of oat beta glucan powder, making them an important resource for functional food development.
Globally, oat beta glucan has become a research and commercial hotspot. In the 1990s, the U.S. FDA officially confirmed that consuming 3 g/day of oat beta glucan or low-fat oat products can reduce blood lipids and decrease cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. Since then, extensive studies have demonstrated that oat beta glucan immune support, blood glucose regulation, gut microbiome improvement, and antioxidant protection contribute to its growing popularity across multiple markets—including functional foods, nutraceuticals, oat beta glucan supplements, and cosmetic formulations.
This article provides an updated analysis of the structure, molecular characteristics, content, biological functions, and food applications of oat beta glucan, offering scientific references for the development of new functional ingredients.
1. Structural Characteristics of Oat Beta Glucan Molecules
Research continues to show that the biological activities of oat beta glucan depend on its molecular structure, molecular weight, content, and linkage patterns. While beta glucans from cereals share similar structural frameworks, variations in β(1→4)/β(1→3) ratios lead to differences in solubility, viscosity, and physiological effects.
The β(1→3) linkages in oat beta glucan introduce molecular flexibility, enabling its well-known thickening and gel-forming properties—key contributors to health effects such as cholesterol lowering, post-prandial glucose modulation, and gut health benefits.
Studies show that approximately 90% of glucose units in oat beta glucan exist in cellotriosyl and cellotetraosyl segments formed through β(1→3) linkages, while the remainder exists as longer cellulose-like regions, indicating a semi-ordered molecular distribution.
Molecular Weight Significance
The weight-average molecular weight determines several functional physicochemical characteristics of oat beta glucan, including:
l solubility
l viscosity
l dispersibility
l gel-forming capacity
Because these properties are closely tied to major health benefits, molecular weight becomes a key factor for oat beta glucan supplement manufacturers and functional food formulators.
Processing methods—such as grinding fineness, temperature, pressure, storage environment, and enzymatic modification—can change the molecular weight of oat beta glucan, thereby altering its bioactivity.
Different cereal sources contain beta glucans with varying molecular weights, but oats typically exhibit the highest range, supporting their superior biological activity.
Table 1. Oat Beta Glucan Content in Various Oat Products
|
Sample |
Oat beta glucan (%) |
|
Oat rice |
3.74 ± 0.05 |
|
Oat flakes |
3.69 ± 0.14 |
|
Oat porridge |
2.88 ± 0.08 |
|
Oat flour |
3.19 ± 0.12 |
|
Oat bran |
3.16 ± 0.08 |
2. Content of Oat Beta Glucan in Oats
Oat beta glucan content is a critical index for the nutritional evaluation and quality control of oat food products. Content levels vary depending on factors such as:
l planting region
l variety
l production year
l agricultural practices
Among these, varietal differences contribute the most variability. Some newly developed cultivars contain 3.0%–5.0% oat beta glucan, making them suitable for high-fiber functional food production.
Table 2. Oat Beta Glucan Content in Different Regions and Years
|
Region |
Content (%) |
|
Gansu |
4.8 ± 0.4 |
|
Shanxi |
4.6 ± 0.4 |
|
Jilin |
4.3 ± 0.8 |
|
Hebei |
4.5 ± 0.7 |
|
Year |
Content (%) |
|
2007 |
4.5 ± 0.5 |
|
2008 |
4.9 ± 0.6 |
|
2009 |
4.5 ± 0.8 |
Breeding high-purity oat beta glucan varieties has become an important direction for agricultural innovation and commercial production.
3. Biological Functions of Oat Beta Glucan
3.1 Cholesterol-Lowering Effect
Clinical studies confirm that daily intake of oat beta glucan 3 g/day significantly reduces LDL-C, non-HDL cholesterol, and apolipoprotein B. The primary mechanism involves:
l increased intestinal viscosity
l reduced bile acid absorption
l enhanced cholesterol breakdown
This makes oat beta glucan immune support and cardiovascular support ingredients a valuable component in functional foods and nutraceuticals.
3.2 Antioxidant Activity
Oat beta glucan helps neutralize free radicals and reduces inflammatory factors. Animal studies indicate improvements in:
l oxidative stress markers
l liver and gastric antioxidant capacity
l lipid peroxidation
These findings support its use in oat beta glucan antioxidant formulas and healthy-aging products.
3.3 Blood Glucose–Lowering Effects
Multiple clinical and meta-analysis results show that consuming oat beta glucan:
l reduces fasting plasma glucose (FPG)
l improves HbA1c
l enhances insulin sensitivity
l reduces post-meal glucose spikes
The mechanism is largely due to the formation of a viscous gel, slowing glucose absorption and extending gastric emptying time.
3.4 Regulation of Gut Microbiota
As a prebiotic fiber, oat beta glucan increases beneficial gut bacteria such as: Bifidobacterium,Lactobacillus.
It also modulates bile acid metabolism and supports short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production, contributing to gut health and immune balance. Enzymatically modified oat beta glucan increases fermentability, making it valuable in infant nutrition, gut health supplements, and functional beverages.
4. Applications in Food Products
Oat beta glucan powder is widely used in:
l yogurts (improving texture and stability)
l baked goods (enhancing volume, moisture, and sensory quality)
l beverages (added viscosity + health claims)
l meat products (improving elasticity, chewiness)
l cosmetic formulations (anti-wrinkle, soothing, moisturizing benefits)
Its compatibility with diverse food systems makes it a versatile ingredient for functional food development, nutraceutical manufacturing, and clean-label product formulations.
5. Outlook
With growing global demand for natural functional ingredients, oat beta glucan is expected to play an increasingly important role across multiple industries. Future research and product innovation may unlock new applications in prebiotics, metabolic health, immune support, and advanced nutraceutical formulations.
As scientific understanding deepens, the commercial potential of oat beta glucan—including high-purity oat beta glucan, water-soluble oat beta glucan, and bulk oat beta glucan powder—will continue to expand.
Contact:
Phone: 0086-13754204265
Tel: 0086-572-2157374
Email: sales@bulkbetaglucan.com
Add: No.235,Huanchengdong Road,Huzhou,Zhejiang,China