Oat beta glucan is a kind of soluble dietary fiber, which mainly exists in the cell wall of oat endosperm and aleurone layer. It is composed of glucose connected by beta (1→3) and beta (1→4) glycosidic bonds. Starch polysaccharide, which has a variety of physiological functions including lowering blood sugar [1-3]. Regular consumption of oatmeal food can effectively reduce the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes and high blood pressure, and its hypoglycemic effect has been recognized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [4]. Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood sugar. According to statistics, the number of adult diabetic patients in the world is increasing year by year (in 2017, there were 451 million people, and it is expected to reach 700 million people in 2045) [5], 90% of which are type 2 diabetes patients [6]. Nutrition therapy plays an extremely important role in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. It can reduce the level of glycosylated hemoglobin in patients with type 2 diabetes by 0.5% to 2.0%[7], and eating fiber-rich foods is one of the typical nutritional treatments. [8-9]. Therefore, eating oat foods rich in oat beta glucan can significantly reduce the blood glucose index of type 2 diabetes.
This article first reviews the effect of oat beta glucan in lowering blood sugar, and then describes the internal structure and external factors that affect the effect of oat beta glucan in lowering blood sugar. Finally, it briefly introduces the effect of oat beta glucan in lowering blood sugar. The mechanism of action, hope to provide a certain reference for follow-up related research.

1.The hypoglycemic effect of oat beta-glucan
Oat beta glucan can lower the glycemic index (GI) of foods. After eating, it can delay the digestion and absorption of starch by reducing the activity of amylase, so as to achieve the effect of lowering blood sugar.
1.1 The effect of oat beta-glucan on food glycemic index
Glycemic index (GI) refers to the ratio of the increase in blood glucose of the body to the increase in blood glucose of standard food (usually glucose) after eating a certain food. Studies have suggested that adding oat beta glucan can significantly reduce the GI value of food[10-12], and1goat beta glucan can reduce the GI of50gcarbohydrates by 4 units [10]. Makelainen et al. [13] and Kim et al. [14] reported that with the increase of oat beta glucan content, the GI of food showed a downward trend [12]. Kim et al. [15] also reported that after the addition of beta glucan, the GI value of starch showed a downward trend as the molecular weight and viscosity increased. This shows that oat beta glucan can significantly reduce GI, and the influence of oat beta glucan on GI is related to factors such as molecular weight and content.
1.2 The effect of oat beta glucan on the body's blood sugar
Postprandial blood glucose, which is the blood glucose level two hours after a meal, is a basic monitoring indicator for the diagnosis of diabetes and has important reference value for improving blood glucose metabolism. Oats are rich in oat beta glucan and have the ability to improve the body's postprandial blood sugar and fasting blood sugar.
Oat beta glucan can significantly reduce the body's postprandial blood sugar. Breakfast cereals rich in4goat beta glucan can reduce blood sugar after a meal by 38% [16]. Bedtime snacks containing1.8goat beta glucan can significantly reduce postprandial blood sugar in children with type 2 diabetes [17]. Adding 6% oat beta glucan to the diet can reduce the postprandial blood glucose level of experimental pigs [18]. Zhang Jie [19] found through in vivo digestion experiments that oat grain beta glucan can effectively reduce the postprandial blood glucose peak in mice. There is a certain dose-effect relationship between the content of oat beta glucan and its blood sugar lowering effect. Zhang Yu [20] pointed out that oat beta glucan has the effect of significantly delaying glucose absorption and reducing postprandial blood glucose, and the molecular weight and content of oat beta glucan can affect postprandial blood glucose. •Mol-1) and high doses (2000 mg•(kg•bw) -1), oat beta glucan has the best effect in reducing postprandial blood sugar. Although high doses (2000 mg•(kg•bw) -1) oat beta glucan can significantly reduce the postprandial blood glucose of experimental type 2 diabetic mice, and with the extension of time, the blood glucose decreases more Obviously, but it cannot be lowered to the normal blood sugar level, which indicates that oat beta glucan can only play an auxiliary hypoglycemic effect [21]. The effect of oat beta glucan on glucose adsorption capacity and glucose diffusion rate is closely related to its ability to reduce postprandial blood sugar in the body. Zhang Yu[20] also pointed out that oat beta glucan with high molecular weight (5 750×103g•mol-1) and high dose (2000mg•(kg•bw) -1) has a good adsorption effect on glucose. It can significantly slow down the diffusion speed of glucose, and the reduction of the body's absorption rate of glucose can also significantly reduce the body's postprandial blood glucose level.
Oat beta glucan can also effectively reduce the body's fasting blood sugar [22]. After administering oat beta glucan to mice for 4 weeks, the fasting blood glucose value of mice showed a downward trend (from 11.8±1.2 mmol•L-1 to 9.8±0.8 mmol•L-1) [20], but another Studies have shown that the effect of oat beta glucan in reducing fasting blood sugar has the lowest threshold (19), and in the case of the same high molecular weight, medium dose (1000 mg• (kg•bw) -1) and high dose ( 2000mg•(kg•bw) -1) oat beta glucan has a stronger ability to lower fasting blood sugar[2].
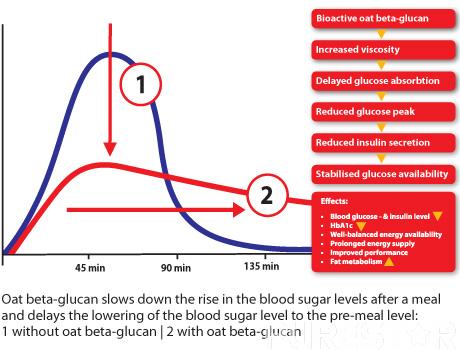
1.3 The effect of enzyme activity and insulin on the body's blood sugar
The speed and degree of starch digestion are the main determinants that affect the blood sugar level in the body [23]. Therefore, reducing the activity of α-amylase and delaying the digestion and absorption of starch can indirectly achieve the effect of lowering blood sugar. Increasing the content of oat beta glucan can inhibit the activity of α-amylase[20], but when the content of oat beta glucan reaches a certain concentration (30mg•mL-1), the inhibition of α-amylase can only be achieved. It has obvious effect [19]. The in vitro starch digestion curve shows that the greater the content of oat beta glucan, the stronger the ability to inhibit starch digestion [20].
Studies have shown that when the activities of invertase and maltase are reduced, the ability of intestinal epithelial cells to absorb glucose is also significantly reduced.Oat beta glucan inhibits the activity of disaccharase to a certain extent, and the high molecular weight (5750×103g•Mol-1) Oat beta glucan has the highest inhibitory efficiency on invertase and maltase, which are 23.15% and 10.40% respectively [20]. Oat beta glucan can effectively inhibit the activity of pepsin, but as the digestion time is prolonged, its inhibitory effect will be weakened [24]. The Na+/K+-ATP enzyme is an indicator reflecting the ability of the small intestine to absorb glucose. Studies have pointed out that oat beta glucan can significantly reduce the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase in the small intestine, that is, reduce the body's ability to absorb glucose, but it does not Shows a dose-effect relationship [20]. In addition, oat beta glucan can inhibit the activity of glucose-6-phosphatase (G-6-Pase), delay the conversion of liver glycogen, and then reduce the body's blood sugar content. 4% oat beta glucan Sugar can make the activity of G-6-Pase show a downward trend [19-20].
Serum insulin is a hormone that can directly lower blood sugar, so the changes in insulin secretion (Fins) can be used to indirectly reflect the effect of oat beta glucan on the body's blood sugar. Wang Haibo [25] reported that after intragastric administration of Yanmai beta glucan in diabetic mice, Fins increased significantly. Cai Fengli[21] found that after 6 weeks of oral administration of oat beta glucan in diabetic mice, the Fins increased significantly, and high-dose (2000mg•(kg•bw) -1) oat beta glucan had the best effect in improving Fins. Good; although oat beta glucan can greatly increase Fins, when the molecular weight is the same, changing the content of oat beta glucan has almost no effect on Fins [20].
2.Influencing factors of oat beta glucan for lowering blood sugar
Oat beta glucan plays a hypoglycemic effect by forming a highly viscous environment in the stomach and intestines. The viscosity of oat beta glucan is determined by its molecular weight and content. Therefore, the hypoglycemic effect of oat beta glucan is related to its structural factors—molecular weight and content. In addition, oat varieties and the processing methods of oat products also have an impact on the hypoglycemic effect of oat beta glucan.
2.1 The effect of the molecular weight and content of oat beta glucan on the effect of lowering blood sugar
The blood sugar lowering performance of oat beta glucan is mainly affected by viscosity, and molecular weight (Mw) and content can affect viscosity [26]. A large number of studies have shown that changes in blood sugar and insulin are related to the content and molecular weight of oat beta glucan, and as the viscosity of foods rich in oat beta glucan increases, its blood sugar lowering effect is significantly enhanced[27], GI Significantly decreased [28]. And the viscosity of beta glucan shows an upward trend with the increase of its molecular weight and content [29]. Therefore, the hypoglycemic ability of oat beta glucan is closely related to its molecular weight and content. The higher the molecular weight of oat beta glucan, the more obvious the effect of reducing fasting blood sugar and controlling blood sugar after meals [20]. Shen Nanhui [30] found that, compared with low molecular weight (Mw=40,000Da) beta glucan beverages, high molecular weight (Mw=70000Da) beta glucan beverages have a better effect on reducing postprandial blood sugar. Lazaridou et al. [31] found that as the molecular weight of beta glucan decreased from 2000kDa to 130kDa, the ability of muffins containing oat beta glucan to lower blood sugar after a meal was significantly weakened (from 45%±6% to 15%). %±6%). Rigand et al. [32] reported that with the increase of the molecular weight of oat beta glucan, the degree of hydrolysis of starch in the in vitro digestion process decreased, thereby achieving the effect of reducing blood sugar.
In addition, the content of oat beta glucan can also affect its viscosity, thereby affecting its blood sugar lowering effect. High-dose oat beta glucan can significantly regulate blood sugar and show a certain dose relationship [33]. The muffin containing8goat beta glucan has a significantly higher blood sugar lowering effect than the muffin containing4goat beta glucan [31]. In addition, when the oat beta glucan/starch ratio was increased from 1.1:10 to 1.6:10, its inhibitory effect on the peak blood sugar was significantly enhanced [32]. However, some studies have pointed out that when the molecular weight is the same, the 250 mL and 600 mL beverages with the same beta glucan content have similar blood sugar lowering effects, which indicates that increasing the viscosity by reducing the volume of the solution has no effect on the blood sugar lowering effect of oat beta glucan. [26].
2.2 The effect of oat beta glucan processing on the effect of lowering blood sugar
The molecular weight of beta glucan depends on the type of oats, growth environment, food matrix and processing process, and the processing process will modify beta glucan, changing its molecular weight and viscosity, and then changing its blood sugar lowering effect ( 34-35]. After the grains of different varieties of naked oats are polished, the content of oat beta glucan in most varieties increases, but the content of a small amount of oat beta glucan decreases. This is due to the hardness and water content of the grains between the varieties. There are differences, and there is serious damage during the polishing process [36]. Tosh et al. [37] reported that processing methods and cooking methods changed the degree of starch gelatinization of 72 kinds of oat foods, which in turn led to greater differences in GI. Granfeldt et al. [38] tested the reaction of 9 elderly people to the consumption of oatmeal, cooked oatmeal, cooked whole oatmeal and white bread, and found that cooked whole oatmeal would lead to lower blood glucose and insulin response after a meal. White bread. The GI value of oatmeal cooked for 80 minutes under normal pressure (62) is greater than that of oatmeal cooked for 20 minutes (49), which indicates that the proportion of water added and the cooking time affect the GI value of oatmeal foods, leading to differences in their hypoglycemic ability [39-40]. The temperature of the paste water also significantly affects the hypoglycemic effect of oat flour. Studies have shown that the higher the final temperature of the paste, the higher the GI value of the oat paste [39]. Because the different processing methods of oatmeal have different effects on the natural physical structural integrity of oats, the structural integrity will affect the GI of oats. For example, the GI of instant oatmeal and instant oatmeal (71 and 75, respectively) are significantly higher than The GI of steel cut oatmeal and thick oatmeal (55 and 53 respectively) [37,41-43]. Fang Haibin et al. [44] reported that after eating barley and oats puffed food, it can effectively inhibit the increase in blood sugar in rats (the blood sugar value dropped from 5.537 mmol•L-1 to 4.834 mmol•L-1). Zhang Yan et al. [45] also found that after oatmeal nests are processed by the "three-cooking" process (fried, scalded, and steamed), frying has a great influence on the beta glucan content of oatmeal nests. The new type of beverage made from oats is an emerging oat food in China, but the content of beta glucan in oat milk made from different varieties of oats is significantly different, and its content ranges from 11.17 to 98.21 mg•(100 mL) -1. The sieving process can reduce the oat beta glucan content of oat milk by 56.32% [46]. Oatmeal is a low-GI food, and its GI is 50.25. Experiments have shown that the postprandial blood glucose (10.25±3.42mmol•L-1) of patients after eating oatmeal is significantly lower than that of ordinary rice (13.01±5.11mmol). •L-1) [41]. Ames et al. [47] compared 92 kinds of oatmeal foods to lower blood sugar, and believed that the blood sugar lowering ability of oat foods depends on the content of beta glucan in the food, the formula of the food, and its processing method.
In summary, the ability of oat beta glucan to lower blood sugar is closely related to the viscosity formed in the solution, and the viscosity of oat beta glucan is determined by its molecular weight. Therefore, the effect of oat beta glucan in lowering blood sugar depends on the viscosity of oat beta glucan. The varieties of oats are also affected by the food processing process.

3.The hypoglycemic mechanism of oat beta glucan
Although it is a difficult problem to study the hypoglycemic mechanism of oat beta glucan, it has very important significance and effect for the rational use of oat beta glucan. The current common oat beta glucan hypoglycemic mechanisms include slowing down gastrointestinal emptying, inhibiting digestive enzyme activity, and improving islet function. The mechanism of slowing down gastrointestinal emptying means that oat beta glucan can form a high-viscosity environment in the gastrointestinal tract, and its higher viscosity can form a physical barrier to hinder the contact between food and digestive enzymes, prolong gastric emptying, and reduce small intestinal contraction Ability to slow down the absorption rate of glucose and achieve the effect of reducing the postprandial blood glucose response [48-50]. Wang Haibo [23] found that oat beta glucan can inhibit the hydrolysis of amylase to reduce blood sugar response. Medium and high doses of oat beta glucan can inhibit the activities of invertase and maltase, slow down starch digestion and absorption and glucose absorption, and indirectly reduce postprandial blood glucose levels [51]. Oat beta glucan can also improve the function of islets and inhibit the release of serum insulin, thereby reducing the burden of islet cells and achieving the effect of lowering blood sugar [25]. Cai Fengli et al. [21] reported that oat beta glucan can improve the pathological structure of the pancreas of experimental type 2 diabetic mice and control the level of apoptosis of islet cells, increase the number of islet cells, thereby increasing the number of islets in diabetic mice. The normal function of cells promotes the secretion of insulin and effectively controls the body's blood sugar balance; at the same time, oat beta glucan can also improve the pathological structure of liver, kidney and pancreas in diabetic mice, and regulate the physiological functions of their important organs. Thereby promoting the synthesis of glycogen, increasing the activity of succinate dehydrogenase in the trihydroxy acid cycle, accelerating the oxidation of succinic acid and reducing the toxic effects of glucose and free fatty acids on islet cells, etc., thereby improving the body's ability to utilize glucose[21] . Zhang Jie et al. [19] found that oat beta glucan can promote glucose degradation by increasing the activity of hepatic glucokinase, increase glycogen synthesis and maintain the binding and sensitivity of insulin to blood glucose molecules, so that the body's blood sugar can maintain a normal level. In addition, Lu Qihong [52] also found that oat beta glucan can improve the damage of pancreatic islet cells through its antioxidant capacity, thereby reducing oxidative damage in diabetic rats. In summary, although there are many researches on the mechanism of oat beta glucan for lowering blood sugar, its hypoglycemic mechanism has not yet reached a conclusion, and further research is needed.
Contact:
Phone: 0086-13754204265
Tel: 0086-572-2157374
Email: sales@bulkbetaglucan.com
Add: No.235,Huanchengdong Road,Huzhou,Zhejiang,China